SpringBoot 缓存 (EhCache 使用)
源文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/u011244202/article/details/55667868
SpringBoot 缓存 (EhCache 2.x 篇)
SpringBoot 缓存
在 Spring Boot 中,通过 @EnableCaching 注解自动化配置合适的缓存管理器(CacheManager),Spring Boot 根据下面的顺序去侦测缓存提供者:
* Generic
* JCache (JSR-107)
* EhCache 2.x
* Hazelcast
* Infinispan
* Redis
* Guava
* Simple
关于 Spring Boot 的缓存机制:
高速缓存抽象不提供实际存储,并且依赖于由 org.springframework.cache.Cache 和 org.springframework.cache.CacheManager 接口实现的抽象。 Spring Boot 根据实现自动配置合适的 CacheManager,只要缓存支持通过 @EnableCaching 注释启用即可。
Spring Boot 配置 EhCache 2.x
官方文档上对于注解缓存的介绍资料非常之少,往往需要我们自己去了解相应的缓存提供者。我这里主要介绍的是 EhCache .
引入依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中引入以下依赖
<!-- 开启 cache 缓存 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>[spring-boot](https://so.csdn.net/so/search?q=spring-boot&spm=1001.2101.3001.7020)-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- ehcache 缓存 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
</dependency> 引入配置文件 ehcache.xml
在 resource 文件夹下创建文件 ehcache.xml,并进行配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"
updateCheck="false">
<defaultCache
eternal="false"
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="0"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" />
<!-- 这里的 users 缓存空间是为了下面的 demo 做准备 -->
<cache
name="users"
eternal="false"
maxElementsInMemory="100"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskPersistent="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="0"
timeToLiveSeconds="300"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" />
</ehcache> ehcache.xml 文件配置详解
diskStore:为缓存路径,ehcache 分为内存和磁盘两级,此属性定义磁盘的缓存位置。
defaultCache:默认缓存策略,当 ehcache 找不到定义的缓存时,则使用这个缓存策略。只能定义一个。
name: 缓存名称。
maxElementsInMemory: 缓存最大数目
maxElementsOnDisk:硬盘最大缓存个数。
eternal: 对象是否永久有效,一但设置了,timeout 将不起作用。
overflowToDisk: 是否保存到磁盘,当系统当机时
timeToIdleSeconds: 设置对象在失效前的允许闲置时间(单位:秒)。仅当 eternal=false 对象不是永久有效时使用,可选属性,默认值是 0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大。
timeToLiveSeconds: 设置对象在失效前允许存活时间(单位:秒)。最大时间介于创建时间和失效时间之间。仅当 eternal=false 对象不是永久有效时使用,默认是 0.,也就是对象存活时间无穷大。
diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据 Whether the disk store persists between restarts of the Virtual Machine. The default value is false.diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:这个参数设置 DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小。默认是 30MB。每个 Cache 都应该有自己的一个缓冲区。
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认是 120 秒。
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当达到 maxElementsInMemory 限制时,Ehcache 将会根据指定的策略去清理内存。默认策略是 LRU(最近最少使用)。你可以设置为 FIFO(先进先出)或是 LFU(较少使用)。
clearOnFlush:内存数量最大时是否清除。
重要:
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy: 可选策略有:LRU(最近最少使用,默认策略)、FIFO(先进先出)、LFU(最少访问次数)。
FIFO,first in first out,先进先出。
LFU, Less Frequently Used,一直以来最少被使用的。如上面所讲,缓存的元素有一个 hit 属性,hit 值最小的将会被清出缓存。
LRU,Least Recently Used,最近最少使用的,缓存的元素有一个时间戳,当缓存容量满了,而又需要腾出地方来缓存新的元素的时候,那么现有缓存元素中时间戳离当前时间最远的元素将被清出缓存。
在主类加上启动注解
在 Spring Boot 主类加上开启缓存的注解 @EnableCaching。
demo : SpringBoot + EhCache
搭建 Spring Boot 工程
我搭建了一个普通的 SpringBoot 工程,配置了 Druid+MySQL。
并在数据库中创建了 users 表,各字段如下:
字段名 属性
id bigint
uuid varchar
name varchar
age int
用户实体类
User.java
public class User {
private long id;
private String uuid;
private String name;
private Integer age;
// 省略 get、set 及 toString 方法
} 用户数据库操作接口
UserDao.java
@Mapper
public interface UserDao{
void delete(String uuid);
User update(User user);
User findByUuid(String uuid);
int save(@Param("user") User user);
} 用户操作 Mapper 文件
UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="qg.fangrui.boot.dao.UserDao">
<!-- 目的:为 Dao 接口方法提供 SQL 语句 -->
<!-- 映射实体对象 -->
<resultMap type="qg.fangrui.boot.model.User">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="uuid" column="uuid" />
<result property="name" column="name" />
<result property="age" column="age" />
</resultMap>
<insert>
INSERT INTO users(name, age, uuid)
VALUES (#{user.name}, #{user.age}, #{user.uuid})
</insert>
<select resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM users WHERE uuid = #{uuid}
</select>
<delete>
DELETE FROM users WHERE uuid = #{uuid}
</delete>
</mapper> 用户操作 service 层
一般情况下,我们在 Sercive 层进行对缓存的操作。先介绍 Ehcache 在 Spring 中的注解:在支持 Spring Cache 的环境下,
- @Cacheable : Spring 在每次执行前都会检查 Cache 中是否存在相同 key 的缓存元素,如果存在就不再执行该方法,而是直接从缓存中获取结果进行返回,否则才会执行并将返回结果存入指定的缓存中。
- @CacheEvict : 清除缓存。
- @CachePut : @CachePut 也可以声明一个方法支持缓存功能。使用 @CachePut 标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中。
- 这三个方法中都有两个主要的属性:value 指的是 ehcache.xml 中的缓存策略空间;key 指的是缓存的标识,同时可以用 # 来引用参数。
UserService.java
@Service
public class UserService {
// 这里的单引号不能少,否则会报错,被识别是一个对象
private static final String CACHE_KEY = "'user'";
private static final String DEMO_CACHE_NAME = "users";
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
// 删除用户数据
@CacheEvict(value = DEMO_CACHE_NAME,key = "'user_'+#uuid")// 这是清除缓存
public void delete(String uuid){
userDao.delete(uuid);
}
// 更新用户数据
@CachePut(value = DEMO_CACHE_NAME,key = "'user_'+#user.getUuid()")
public User update(User user) throws CacheException{
User user1 = userDao.findByUuid(user.getUuid());
if (null == user1){
throw new CacheException("Not Find");
}
user1.setAge(user.getAge());
user1.setName(user.getName());
return user1;
}
// 查找用户数据
@Cacheable(value=DEMO_CACHE_NAME,key="'user_'+#uuid")
public User findByUuid(String uuid){
// 若找不到缓存将打印出提示语句
System.err.println("没有走缓存!"+uuid);
return userDao.findByUuid(uuid);
}
// 保存用户数据
@CacheEvict(value=DEMO_CACHE_NAME,key=CACHE_KEY)
public int save(User user){
return userDao.save(user);
}
} Controller 类
最后我们创建一个 Controller 来访问我们的缓存。因为我的 SpringBoot 处于 Debug 模式,会将所有的数据库操作打印出来,这样子缓存作用就可一目了然了。
EhcacheController.java
@RestController
public class EhcacheController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EhcacheController.class);
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/encache")
public String EhcacheTest(){
logger.debug("进行 Encache 缓存测试");
System.out.println("==== 生成第一个用户 ====");
User user1 = new User();
// 生成第一个用户的唯一标识符 UUID
String u1_uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// 去掉 UUID 的 - 符号
String uuid1 = u1_uuid.substring(0,8)+u1_uuid.substring(9,13)+u1_uuid.substring(14,18)+u1_uuid.substring(19,23)+u1_uuid.substring(24);
user1.setName("张三");
user1.setAge(18);
user1.setUuid(uuid1);
if (userService.save(user1) == 0){
throw new JdbcException("用户对象插入数据库失败");
}
// 第一次查询
System.out.println(userService.findByUuid(user1.getUuid()));
// 通过缓存查询
System.out.println(userService.findByUuid(user1.getUuid()));
System.out.println("==== 修改数据 ====");
User user2 = new User();
user2.setName("李四 - update");
user2.setAge(22);
user2.setId(user1.getId());
user2.setUuid(user1.getUuid());
try {
System.out.println(userService.update(user2));
} catch (CacheException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(userService.findByUuid(user2.getUuid()));
return "success";
}
} 测试
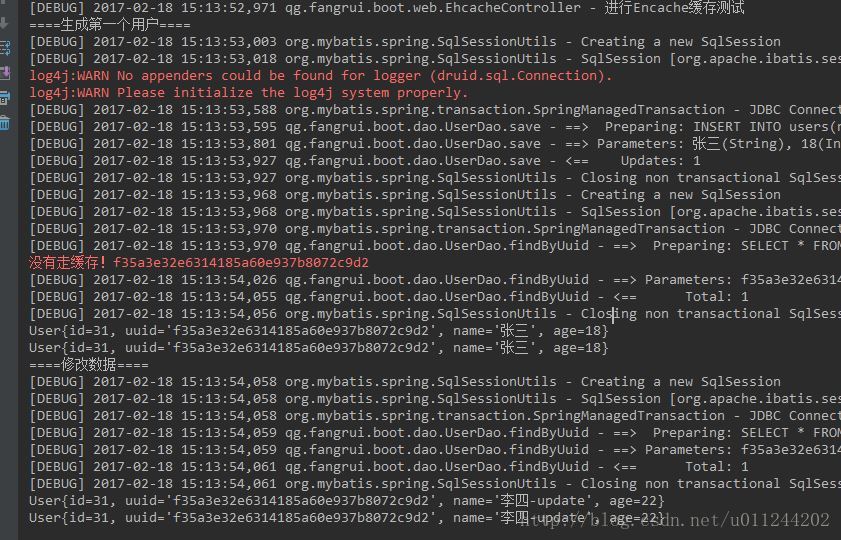
启动 SpringBoot 工程,访问 http://localhost:8080/encache ,并查看控制台打印信息:
由控制台,我们可以清楚到看到,第一次查询用户信息时,工程将用户信息存入缓存中;在第二次查询时,无需访问数据库直接从缓存中获取用户信息。